What is UPS?
-Working & Types of UPS Explained
This article
explains the UPS, its application, historical background, types and working
principle of UPS with their schematic diagram.
Definition:
A UPS is a device
which provides an uninterruptable power supply so as to maintain the continuity
of supply in case of power outage. UPS stands for Uninterruptable Power Supply.
Requirement
of UPS:
There are several
applications where even a temporary power failure can cause a great deal of
public inconvenience leading to large economic losses. Examples of such
applications are major computer installations, process control in chemical
plant, safety monitors, general communication systems, hospital intensive care
units (ICUs) etc. For such critical loads, it is of paramount importance to
provide an uninterruptable power supply. Here, comes the importance of UPS.
Application of UPS system caters to such critical loads.
Background:
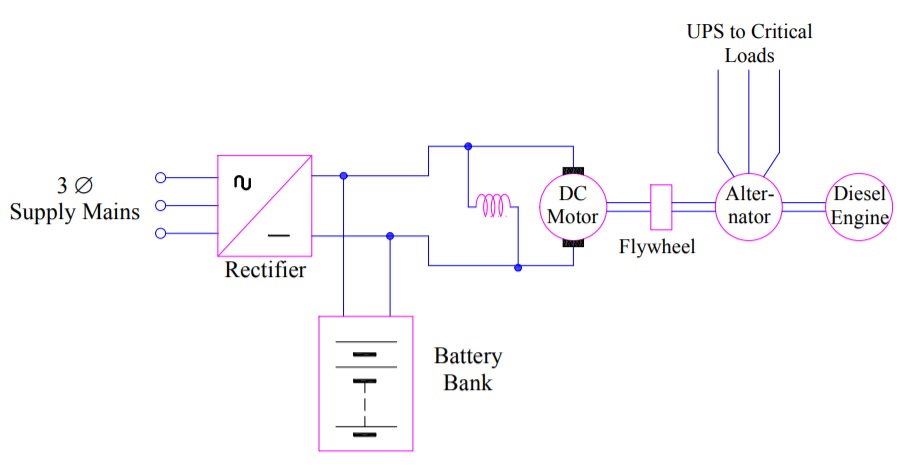
UPS system used
earlier were based on an arrangement of DC Motor, Alternator and DG Set. This
arrangement is shown below.
This arrangement
consists of DC motor driven alternator, the shaft of
which is also connected to diesel engine. The three phase main supply, after
rectification, charges a DC battery bank and feeds the DC motor as well. The
uninterruptable power supply needed is driven from the alternator output
terminals as shown in the figure.
When main supply
fails, the diesel engine is rub to take over the loads. Since, the starting of
diesel engine takes around 10 to 20 seconds, battery bank provides the required
power supply to the load during these 10 to 20 seconds with the help of DC
motor and fly-wheel. In this way, no-break power supply is extended to the
critical loads.
However, this
arrangement of UPS system is not used now a day. Static UPS system are more
popular these days up to few kVA ratings.
Types of UPS:
The static UPS are
of two types:
·
Short-break UPS
·
No-break UPS
In short-break UPS,
the load gets disconnected from the power source for a short duration of the
order of 4 to 5 ms. For this period, no supply is available to the load.
In no-break UPS,
load gets continuous uninterrupted power supply from the power source. There is
no any interruption in power supply in no-break UPS. Such UPS are mostly used
for large computer installation. In computer installation, a break of power
supply of the order of 4 to 5ms is not tolerable at all and hence no-break UPS
is the right choice for such applications.
Working of UPS:
The working
principle of short-break and no-break UPS is discussed along with schematic
diagram in the following section.
Short-Break UPS and
its Working:
In short-break UPS,
the load gets disconnected from the power source for a short duration of the
order of 4 to 5 ms. This type of UPS is suitable for applications where short
interruption of the order of 4-5 ms is tolerable.
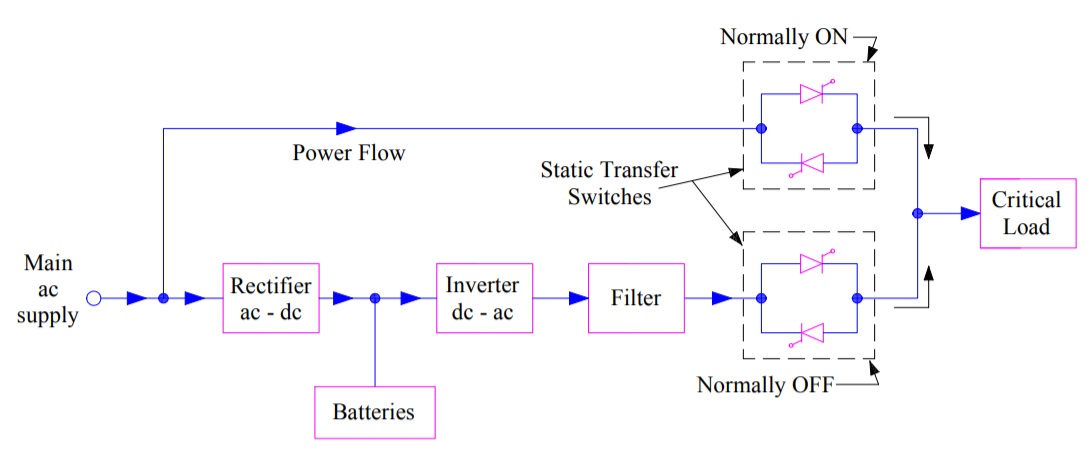
A simple schematic
diagram of short-break UPS is shown in figure below.
A careful
observation of the schematic reveals the technology behind this UPS system. As
evident, main AC supply is rectified to DC. This DC output from the rectifier
charges the batteries and is also converted to AC by an inverter. After passing
through the filter, AC can be delivered to the load in case normally OFF
contacts are closed.
Under normal
operating condition, normally ON contacts are closed and normally OFF contacts
are open. Therefore, the power supply to load is extended via main AC supply under
normal condition. However, in case of power outage, normally OFF contacts
become closed & normally ON contacts become open. This changeover takes
time of 4-5 ms. Hence, during this period, load is neither connected to the
main AC source (main AC is not available due to power outage) nor the inverter output. Once
normally OFF contact becomes closed, load received power from the inverter and
filter.
A momentary interruption
in the supply to the load can be observed in case lamps and fluorescent tubes
are a part of load. When normally-ON switch is opened and
normally OFF switch is turned ON, lamps will have a transient dip in their
illumination whereas fluorescent tubes will be OFF momentarily and the get
turned on again.
When the main AC
supply is resumed, critical loads get connected to the main AC supply source
through normally ON switch. Again, momentarily interruption in illumination is
observed. This arrangement of short-break UPS is also known as stand-by power
supply.
No-break UPS and
its Working:
In no-break UPS,
load gets continuous uninterrupted power supply from the power source. There is
no any interruption in power supply in this uninterruptible power supply
system. Simple schematic diagram of no-break UPS is shown below.
In this system,
main AC supply is rectified and the rectifier delivers
power to maintain the required charge on the batteries. Rectifier
also supplies power to the inverter continuously which in turn extend power to
the load through filter and normally ON switch. Thus, the load is connected to
the inverter all the time. This simply means that, power supply to the load is
extended from battery power. Though battery receives power from main AC supply
but in the event of power outage, the battery will deliver power to the load
without interruption as per its rated capacity.
Rated capacity of
batter is given in terms of AH (Ampere Hour). If this is 20AH, this means
battery can deliver 2 A of current for 10 hours or 4 A of current for 5 hours
or 10 A of current for 2 hours.
So, you might think
when main AC supply is connected to the load through normally OFF switch? Let us
discuss this requirement.
In case inverter
failure is detected, the load is switched ON to the main AC supply by turning
ON the normally OFF switch and opening the normally ON switch. The transfer of
load from inverter to main AC supply takes 4-5 ms as compared to 40-50 ms for a
mechanical contactor. is the reason,
main AC supply is connected to load through normally OFF switch.
After inverter
fault is cleared, uninterruptible power supply is again restored to the load
through normally ON switch. The batteries are now recharged from the main AC
supply by adjusting the charge at maximum charge rate so that batteries are
charged to their full capacity in the shortest possible time.
Advantage of
No-break UPS:
Following are the
main advantages of no-break UPS:
·
The
inverter can be used to condition the supply delivered to load.
·
Load
is always protected from the transient that may occur in the main AC supply.
Hence, life of connected load is enhanced.
·
Inverter
output frequency can be maintained at the desired value.

Comments